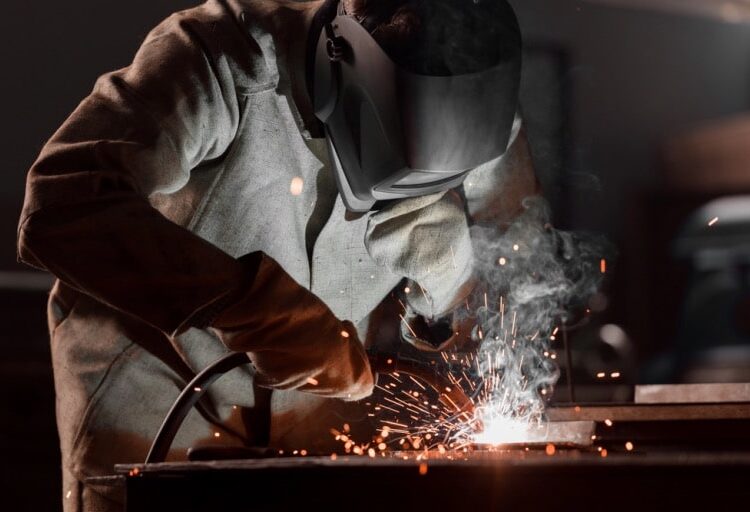
Manufacturing environments are inherently risky, with workers often exposed to high temperatures, dangerous machinery, and hazardous materials. Burns and heat-related injuries are among the most common risks, particularly in industries that involve metalworking, welding, and chemical processing. These types of injuries can range from minor burns to severe third-degree burns or even heatstroke, requiring immediate medical attention and long-term recovery.
Preventing burns and heat-related injuries is crucial for maintaining worker safety in the manufacturing sector. Employers must take proactive measures to reduce these risks by implementing safety protocols, ensuring proper training, and providing the necessary protective equipment. Workers also need to be aware of potential hazards and follow safety guidelines to avoid dangerous situations.
Identifying Common Sources of Burns in Manufacturing
Burn injuries in manufacturing are often the result of direct exposure to hot surfaces, open flames, steam, or hazardous chemicals. Workers may encounter these hazards when working with furnaces, welding equipment, or industrial ovens. Contact burns from touching hot surfaces, thermal burns from exposure to high temperatures, and chemical burns from handling caustic substances are all common in manufacturing settings.
In addition to physical contact burns, explosions, and electrical hazards also pose significant risks. Faulty machinery, improper handling of flammable materials, and inadequate safety precautions can lead to accidents, resulting in serious injuries. Identifying these risks is the first step in implementing measures to protect workers from harm.
The Importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for preventing burns and heat-related injuries in manufacturing environments. Items such as heat-resistant gloves, aprons, face shields, and safety goggles are designed to protect workers from direct exposure to high temperatures, hot surfaces, and hazardous chemicals. Proper use of PPE can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Employers must ensure that workers have access to the appropriate PPE for their specific tasks and that the equipment is maintained in good condition. Workers should be trained on how to properly wear and use PPE, as improper usage can lead to exposure and injury. Regular inspections and replacements of PPE are also necessary to ensure continued protection in hazardous environments.
Implementing Safety Protocols and Training
Preventing burns and heat-related injuries in manufacturing requires more than just providing protective equipment. Comprehensive safety protocols must be in place, including guidelines for handling hazardous materials, operating machinery, and managing emergency situations. These protocols should be tailored to the specific hazards of each manufacturing environment.
Training programs are essential for ensuring that workers understand these safety protocols and can apply them effectively. Workers need to be educated on the proper handling of hot materials, the importance of maintaining safe distances from heat sources, and the correct procedures for managing chemical spills or fire emergencies. Ongoing training and regular safety drills help reinforce these protocols and keep workers prepared for potential hazards.
Heat-Related Illnesses: Recognizing the Signs
In manufacturing environments, especially during warmer months or in consistently hot facilities, heat-related illnesses are a serious risk. Below is a list of key points to recognize and prevent these conditions:
- Heat Exhaustion: Common symptoms include dizziness, excessive sweating, nausea, and a rapid pulse, indicating the body is struggling to cool down.
- Heatstroke: A more severe condition that can be life-threatening if not treated immediately, characterized by confusion, dry skin, high body temperature, and loss of consciousness.
- Dehydration and Fatigue: Prolonged exposure to extreme heat without adequate hydration can lead to exhaustion, reducing a worker’s ability to perform tasks safely.
Emergency Response Procedures for Burn Injuries
In the event of a burn injury, quick and effective emergency response can make a significant difference in the severity of the injury and the outcome of the worker’s recovery. All manufacturing facilities should have clearly defined emergency response procedures in place, including first aid for burns, evacuation plans, and access to medical care.
Workers should be trained to respond to burn injuries by cooling the affected area, applying sterile dressings, and seeking immediate medical attention. In cases of chemical burns, it is essential to flush the area with water and remove any contaminated clothing. Quick action can help minimize the damage and prevent further complications.
Regular Maintenance of Machinery and Equipment
One of the most effective ways to prevent burns and heat-related injuries in manufacturing is through the regular maintenance of machinery and equipment. Faulty or poorly maintained equipment is a leading cause of accidents that result in burns. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance help identify potential hazards before they lead to an injury.
Machinery that generates heat, such as industrial ovens or welding equipment, should be regularly checked for malfunctions or signs of wear. Proper ventilation systems should also be maintained to reduce the buildup of heat in enclosed spaces. Ensuring that equipment is in good working condition reduces the risk of accidents and protects workers from unnecessary exposure to dangerous temperatures.
Protecting Workers’ Rights After an Injury
Despite preventive measures, accidents can still happen, and when they do, workers have the right to seek compensation for their injuries. Burn and heat-related injuries can lead to significant medical bills, lost wages, and long-term disabilities. Workers may be entitled to compensation through workers’ compensation claims or, in cases of negligence, through legal action against the employer or equipment manufacturer.
Consulting with an injury lawyer can provide injured workers with valuable information about their legal options and ensure they receive the compensation they are entitled to. A free consultation with an injury lawyer can help workers understand their rights, explore the possibility of filing a claim, and navigate the complexities of the legal system while focusing on recovery.
The Role of Workplace Culture in Preventing Injuries
Workplace culture plays a significant role in preventing burns and heat-related injuries in manufacturing settings. A strong safety culture prioritizes the well-being of workers and encourages proactive measures to avoid accidents. In a positive safety environment, employees feel empowered to report potential hazards, participate in safety drills, and follow established protocols without fear of reprisal or negligence.
Leadership within the company sets the tone for this culture. When employers emphasize the importance of safety, provide regular training, and reward safe practices, workers are more likely to adhere to safety guidelines and remain vigilant in identifying risks.